基于物理模型和全局优化算法的叶面积指数反演
遥感生物物理参数反演是遥感观测中非常重要的一项问题,今天我们花点时间来实现这一目标。
1 核心目标
(1)掌握基于物理模型的遥感参数反演的流程并能够独立完成参数反演。
(2)了解使用全局优化算法进行生物物理参数反演问题求解的思路。
2 主要内容
(1)任选两个不同植被类型站点,反演与地面测量数据对应时间的站点周围小区域LAI,并与基于地面测量数据的LAI进行对比分析。
(2)反演站点对应像元任意一年的LAI,并与MODIS LAI对比分析。
3 前期准备
(1)数据准备
站点数据下载:选择两个不同的植被类型的站点。本次选择的是代表森林的比利时的Sonian forest站点,以及代表草地的位于尼日尔的WANKAMA站点作为案例来进行讲解。
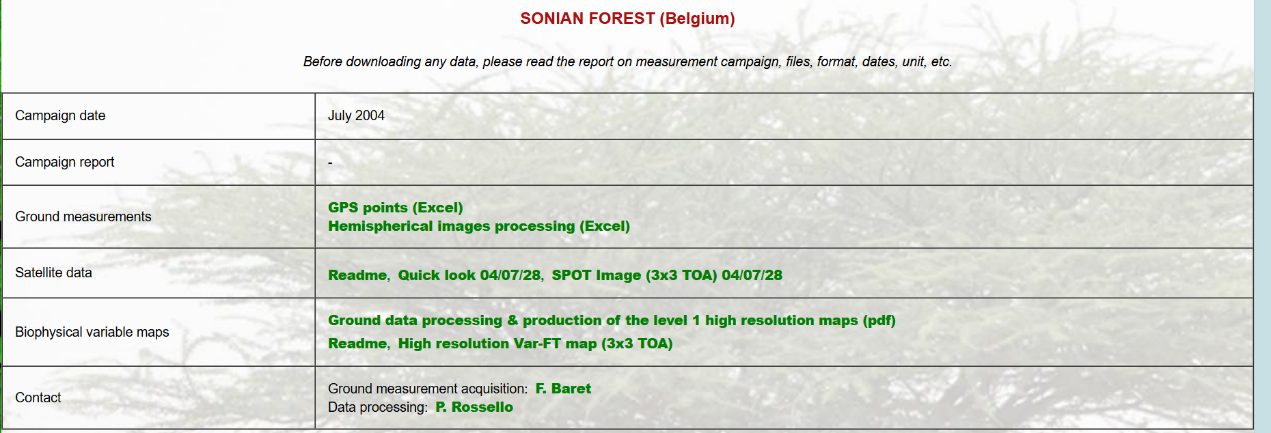
图 站点信息1
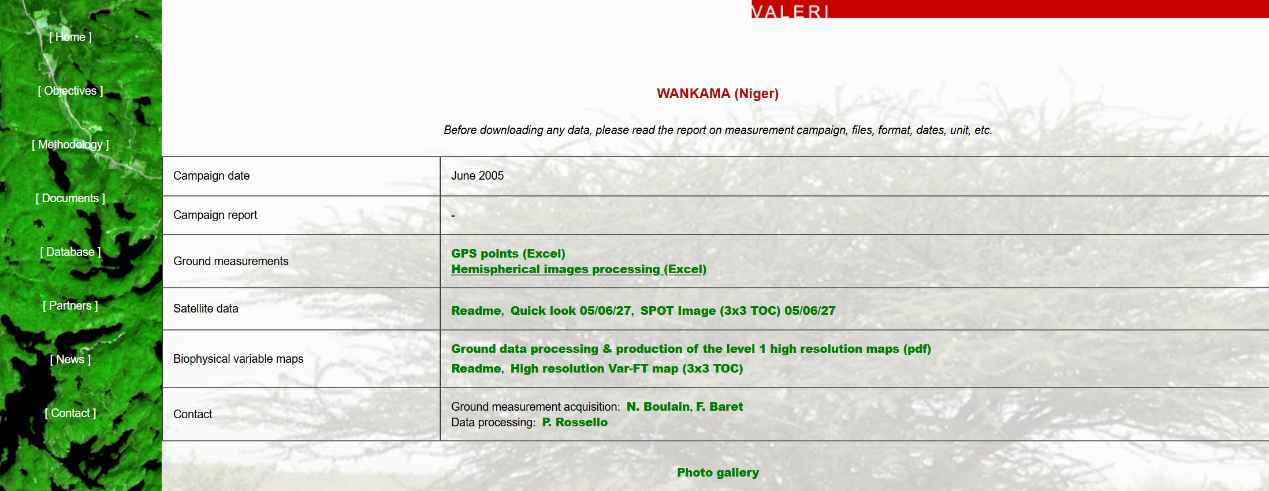
图 站点信息2
网站地址:http://w3.avignon.inra.fr/valeri/fic_htm/database/main.php.
这两个站点分别提供了UTM投影WGS-84坐标系下若干点的地面测量数据,包含有效LAI值和真实LAI值。该数据可用于后续反演LAI的精度验证。
MODIS数据下载:
首次下载,利用Global Subsets Tool工具下载小区域两个站点对应日期的地表反射率数据- MOD09A1和叶面积指数数据- MOD15A2H。两个数据的空间分辨率都是500m,由8天合成,由tif格式存储。同时下载该区域的2000-2020年MODIS的叶面积指数作为先验信息。
网站地址:TESViS Subset Order History,结果发现这个网站还是有点小问题,下载出来的影像的时间和站点观测的时间不对,这可能会影响后续的反演。
辗转多次,后面前往Google Earth Engine网站下载MODIS数据。基本流程是通过GEE平台,以站点的经纬度为中心,创建5km×5km的正方形区域,调用MODIS的反射率数据和叶面积指数产品,分别完成缩放因子操作,还原数据的数值。同时,在平台上选择站点记录的日期的每年的LAI数据,每一年在 站点观测数据对应日期附近20天窗口内的所有LAI影像先做年内平均,再对2002-2025年计算多年平均值,作为LAI反演的先验信息。
时间序列数据下载:使用Google Earth Engine网站提取Sonian forest站点所在像元的MOD09A1数据的七个波段的反射率数据和MOD15A2H的叶面积指数数据,并以表格的形式存储。
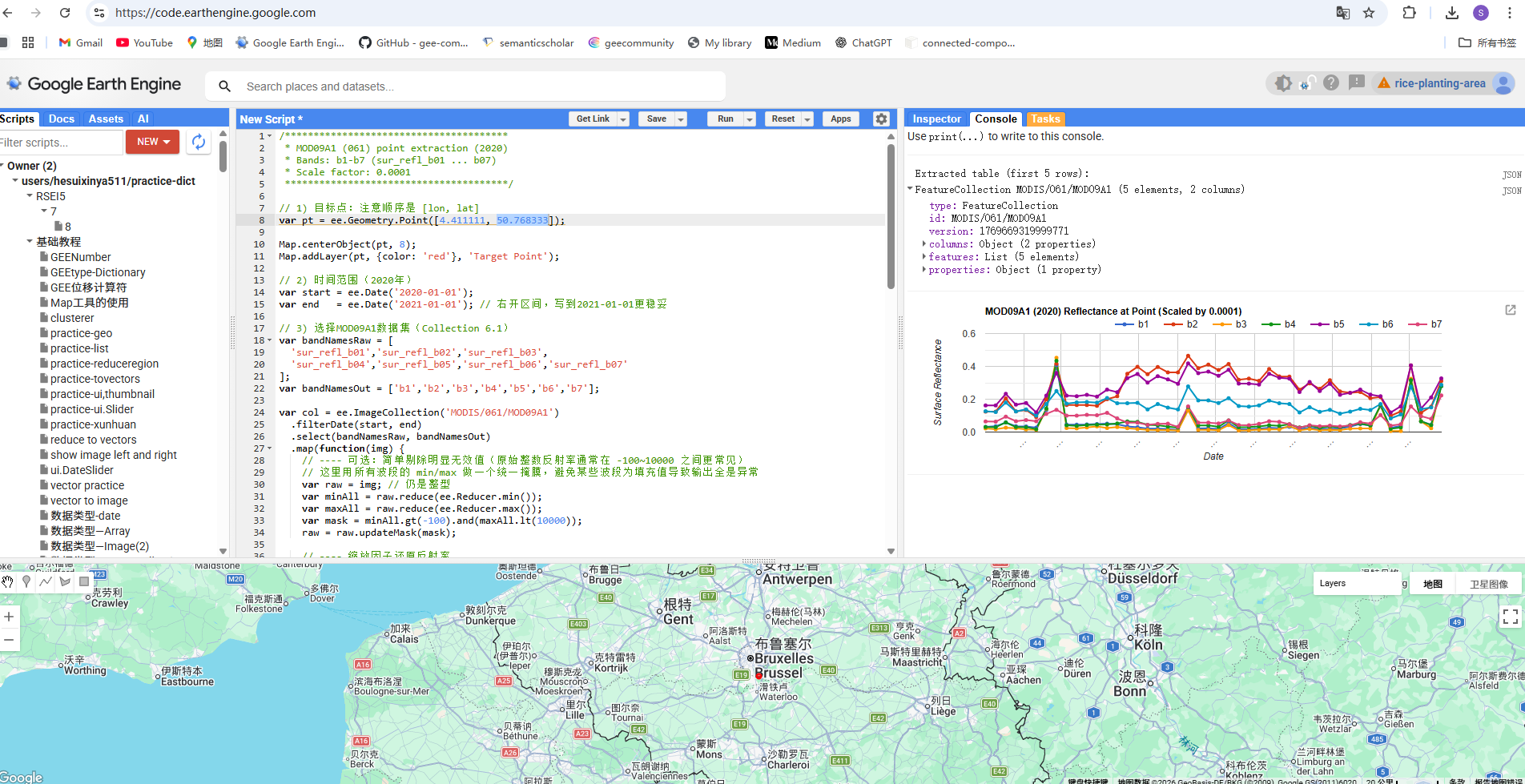
图 GEE下载站点所在像元一年七个波段的反射率数据
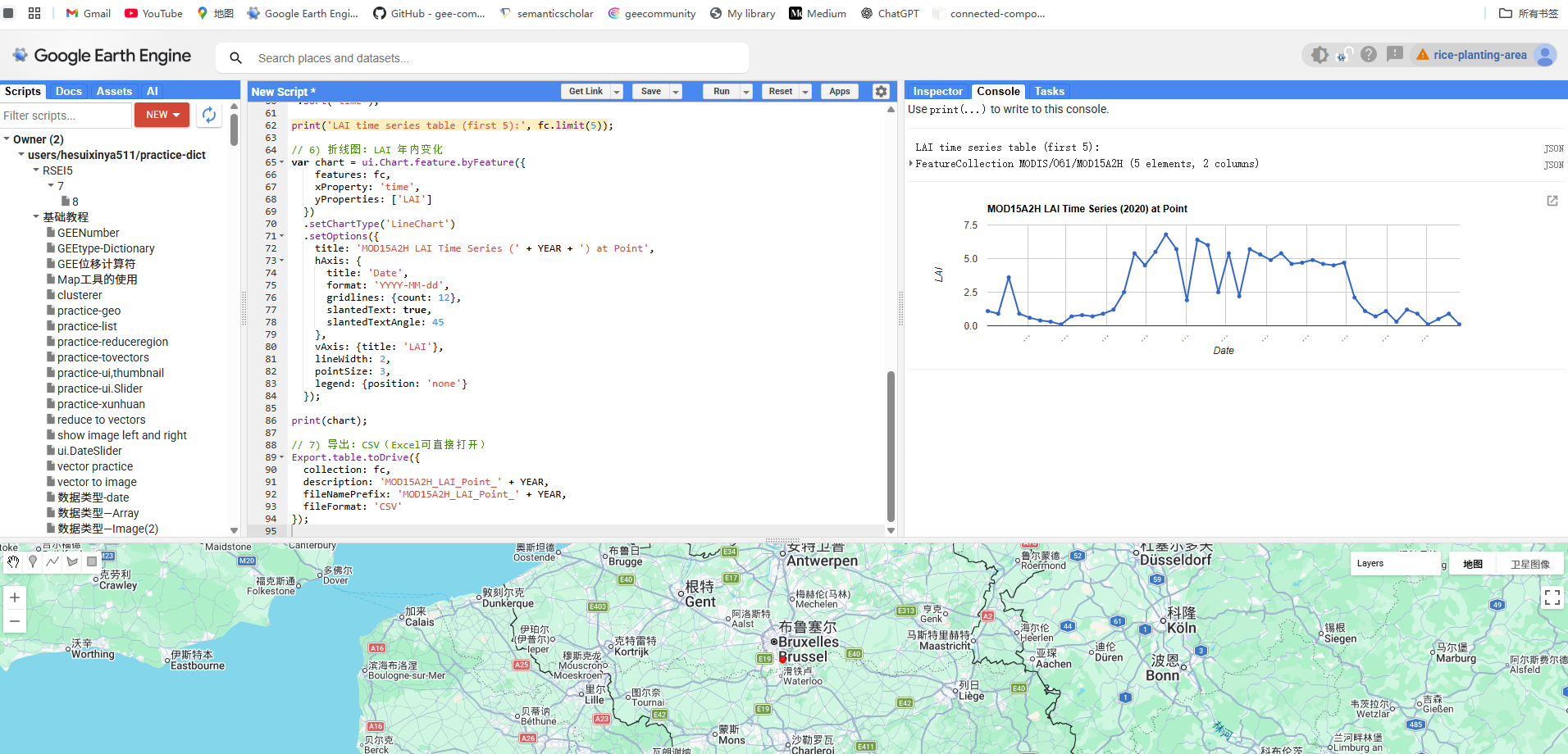
图 GEE下载站点所在像元一年的LAI数据
下载数据的代码也提供给你了,首先是下载小区域的地表反射率数据和MODIS叶面积指数产品的代码:
/*************************************************
* ROI: 5km x 5km centered at (50.768333N, 4.411111E)
* (1) MOD09A1 near 2004-06-21: b1-b7 scaled (0.0001), export 7 tif (one band each)
* (2) MOD15A2H near same period: LAI scaled (0.1), export tif
* (3) MOD15A2H prior LAI mean (2002-2025): for EACH year,
* mean of ALL LAI images within 6/21 ± windowDays, then multi-year mean -> export tif
*
* Robust strategy:
* - Export: DO NOT use clip(); use Export.region to crop (stable)
* - Visualization: reproject to EPSG:4326 then clip(roi) for map display
*************************************************/
// =====================
// 0) Parameters
// =====================
var lon = 2.635278;
var lat = 13.645;
var targetDateStr = '2005-06-27'; // target date "near"
var windowDays = 20; // "near" window in days (8-day products: 8~24)
var roiSizeKm = 5;
var halfSizeM = roiSizeKm * 1000 / 2;
var exportScale = 500;
var exportCRS = 'EPSG:4326';
// prior window mean years
var priorStartYear = 2002;
var priorEndYear = 2025;
// =====================
// 1) ROI in EPSG:4326 rectangle (geodesic=false)
// =====================
var pt = ee.Geometry.Point([lon, lat]);
var dLat = halfSizeM / 111320;
var dLon = halfSizeM / (111320 * Math.cos(lat * Math.PI / 180));
var roi = ee.Geometry.Rectangle(
[lon - dLon, lat - dLat, lon + dLon, lat + dLat],
null,
false // geodesic=false
);
// Display ROI outline
Map.centerObject(roi, 10);
Map.addLayer(ee.Image().byte().paint(roi, 1, 2), {palette:['yellow']}, 'ROI (5km×5km)');
Map.addLayer(pt, {color:'red'}, 'Center Point');
// =====================
// 2) Helper: choose closest image within +/- windowDays
// =====================
function getClosestImage(ic, targetDate, windowDays) {
var t = ee.Date(targetDate);
var filtered = ic.filterDate(t.advance(-windowDays, 'day'), t.advance(windowDays, 'day'));
var withDelta = filtered.map(function(img) {
var delta = ee.Number(img.get('system:time_start')).subtract(t.millis()).abs();
return img.set('delta', delta);
});
return ee.Image(withDelta.sort('delta').first());
}
// Helper: for map display only (reproject then clip)
function vizClip(img, region, scale) {
return img
.resample('bilinear')
.reproject({crs: exportCRS, scale: scale})
.clip(region);
}
// =====================
// 3) (1) MOD09A1 reflectance b1-b7 near target date
// =====================
var mod09BandsRaw = [
'sur_refl_b01','sur_refl_b02','sur_refl_b03','sur_refl_b04',
'sur_refl_b05','sur_refl_b06','sur_refl_b07'
];
var mod09BandsOut = ['b1','b2','b3','b4','b5','b6','b7'];
var mod09IC = ee.ImageCollection('MODIS/061/MOD09A1')
.select(mod09BandsRaw, mod09BandsOut);
var mod09Raw = getClosestImage(mod09IC, targetDateStr, windowDays);
var mod09Date = ee.Date(mod09Raw.get('system:time_start'));
print('Selected MOD09A1 nearest date:', mod09Date);
// Simple valid mask (avoid fill/abnormal)
var mod09Min = mod09Raw.reduce(ee.Reducer.min());
var mod09Max = mod09Raw.reduce(ee.Reducer.max());
var mod09Valid = mod09Min.gt(-100).and(mod09Max.lt(10000));
// Scale factor 0.0001
var mod09Scaled = mod09Raw.updateMask(mod09Valid)
.multiply(0.0001)
.toFloat();
// Map display
var mod09Show = vizClip(mod09Scaled, roi, exportScale);
Map.addLayer(mod09Show.select(['b1','b4','b3']), {min:0, max:0.4}, 'MOD09A1 TrueColor (scaled, ROI)');
mod09BandsOut.forEach(function(b){
Map.addLayer(mod09Show.select(b), {min:0, max:0.5}, 'MOD09A1 '+b+' (scaled, ROI)');
});
// Export: one band one tif (NO clip; crop by region)
mod09BandsOut.forEach(function(b){
Export.image.toDrive({
image: mod09Scaled.select(b),
description: 'MOD09A1_near_' + targetDateStr.replace(/-/g,'') + '_ROI5km_' + b,
fileNamePrefix: 'MOD09A1_near_' + targetDateStr.replace(/-/g,'') + '_ROI5km_' + b,
region: roi,
scale: exportScale,
crs: exportCRS,
maxPixels: 1e13
});
});
// =====================
// 4) (2) MOD15A2H LAI near SAME PERIOD (use MOD09 selected date as target)
// =====================
var mod15IC_raw = ee.ImageCollection('MODIS/061/MOD15A2H')
.select(['Lai_500m']);
var mod15Raw = getClosestImage(mod15IC_raw, mod09Date, windowDays);
var mod15Date = ee.Date(mod15Raw.get('system:time_start'));
print('Selected MOD15A2H nearest date:', mod15Date);
// LAI valid range raw: 0~100 (scaled 0~10)
var laiRaw = mod15Raw.select('Lai_500m');
var laiValid = laiRaw.gte(0).and(laiRaw.lte(100));
// Scale factor 0.1
var laiScaled = laiRaw.updateMask(laiValid)
.multiply(0.1)
.rename('LAI')
.toFloat();
// Map display
var laiShow = vizClip(laiScaled, roi, exportScale);
Map.addLayer(laiShow, {min:0, max:6}, 'MOD15A2H LAI (scaled, ROI)');
// Export LAI tif (NO clip; crop by region)
Export.image.toDrive({
image: laiScaled,
description: 'MOD15A2H_LAI_near_' + targetDateStr.replace(/-/g,'') + '_ROI5km',
fileNamePrefix: 'MOD15A2H_LAI_near_' + targetDateStr.replace(/-/g,'') + '_ROI5km',
region: roi,
scale: exportScale,
crs: exportCRS,
maxPixels: 1e13
});
// =====================
// 5) (3) Prior LAI mean (2002-2025):
// For EACH year, mean of ALL images in 6/21 ± windowDays,
// then multi-year mean
// =====================
// Build a scaled+masked MOD15A2H LAI collection once
var mod15ScaledIC = ee.ImageCollection('MODIS/061/MOD15A2H')
.select(['Lai_500m'])
.map(function(img) {
var raw = img.select('Lai_500m');
var valid = raw.gte(0).and(raw.lte(100));
var lai = raw.updateMask(valid)
.multiply(0.1)
.rename('LAI')
.toFloat();
return lai.copyProperties(img, ['system:time_start']);
});
var years = ee.List.sequence(priorStartYear, priorEndYear);
// For each year: take ALL images within window -> mean
var perYearImgs = years.map(function(y) {
y = ee.Number(y);
var t = ee.Date.fromYMD(y, 6, 21);
var ic = mod15ScaledIC.filterDate(
t.advance(-windowDays, 'day'),
t.advance(windowDays, 'day')
);
var n = ic.size();
// If no image, return fully-masked image to avoid errors
var yearlyMean = ee.Image(ee.Algorithms.If(
n.gt(0),
ic.mean(),
ee.Image.constant(0).rename('LAI').updateMask(ee.Image.constant(0))
));
return yearlyMean
.set('year', y)
.set('n_in_window', n)
.set('system:time_start', t.millis());
});
var perYearIC = ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(perYearImgs);
// Check counts (should typically be >0)
print('Per-year image counts around 6/21 (2002-2025):',
perYearIC.aggregate_array('n_in_window'));
// Multi-year mean
var laiPriorMean = perYearIC.mean()
.rename('LAI_prior_mean_2002_2025')
.toFloat();
// Map display
var priorShow = vizClip(laiPriorMean, roi, exportScale);
Map.addLayer(priorShow, {min:0, max:6}, 'LAI Prior Mean 2002-2025 (ROI)');
// Export prior mean tif (NO clip; crop by region)
Export.image.toDrive({
image: laiPriorMean,
description: 'MOD15A2H_LAI_priorMean_2002_2025_near_0621_ROI5km',
fileNamePrefix: 'MOD15A2H_LAI_priorMean_2002_2025_near_0621_ROI5km',
region: roi,
scale: exportScale,
crs: exportCRS,
maxPixels: 1e13
});
提取某个点的MODIS反射率产品的时间序列代码:
/***************************************
* MOD09A1 (061) point extraction (2020)
* Bands: b1-b7 (sur_refl_b01 ... b07)
* Scale factor: 0.0001
***************************************/
// 1) 目标点:注意顺序是 [lon, lat]
var pt = ee.Geometry.Point([2.635278, 13.645]);
Map.centerObject(pt, 8);
Map.addLayer(pt, {color: 'red'}, 'Target Point');
// 2) 时间范围(2020年)
var start = ee.Date('2020-01-01');
var end = ee.Date('2021-01-01'); // 右开区间,写到2021-01-01更稳妥
// 3) 选择MOD09A1数据集(Collection 6.1)
var bandNamesRaw = [
'sur_refl_b01','sur_refl_b02','sur_refl_b03',
'sur_refl_b04','sur_refl_b05','sur_refl_b06','sur_refl_b07'
];
var bandNamesOut = ['b1','b2','b3','b4','b5','b6','b7'];
var col = ee.ImageCollection('MODIS/061/MOD09A1')
.filterDate(start, end)
.select(bandNamesRaw, bandNamesOut)
.map(function(img) {
// ---- 可选:简单剔除明显无效值(原始整数反射率通常在 -100~10000 之间更常见)
// 这里用所有波段的 min/max 做一个统一掩膜,避免某些波段为填充值导致输出全是异常
var raw = img; // 仍是整型
var minAll = raw.reduce(ee.Reducer.min());
var maxAll = raw.reduce(ee.Reducer.max());
var mask = minAll.gt(-100).and(maxAll.lt(10000));
raw = raw.updateMask(mask);
// ---- 缩放因子还原反射率
var scaled = raw.multiply(0.0001);
return scaled.copyProperties(img, ['system:time_start']);
});
// 4) 将每期影像在点位处取值,组织成 FeatureCollection
var fc = ee.FeatureCollection(
col.map(function(img) {
var t = ee.Number(img.get('system:time_start'));
var dateStr = ee.Date(t).format('YYYY-MM-dd');
// point extraction:用 first() 在点上取像元值
var vals = img.reduceRegion({
reducer: ee.Reducer.first(),
geometry: pt,
scale: 500, // MOD09A1 500m
maxPixels: 1e13
});
return ee.Feature(null, vals)
.set('time', t) // 用于时间轴
.set('date', dateStr); // 导出更友好
})
)
// 如果某些日期点位被云/掩膜导致为空,这里过滤掉
.filter(ee.Filter.notNull(bandNamesOut))
.sort('time');
print('Extracted table (first 5 rows):', fc.limit(5));
// 5) 折线图:7个波段随时间变化
var chart = ui.Chart.feature.byFeature({
features: fc,
xProperty: 'time',
yProperties: bandNamesOut
})
.setChartType('LineChart')
.setOptions({
title: 'MOD09A1 (2020) Reflectance at Point (Scaled by 0.0001)',
hAxis: {
title: 'Date',
format: 'YYYY-MM-dd',
gridlines: {count: 12},
slantedText: true,
slantedTextAngle: 45
},
vAxis: {title: 'Surface Reflectance'},
lineWidth: 2,
pointSize: 3,
legend: {position: 'right'}
});
print(chart);
// 6) 导出表格到Google Drive(CSV 可直接用 Excel 打开)
Export.table.toDrive({
collection: fc,
description: 'MOD09A1_Point_2020_b1_b7_scaled',
fileNamePrefix: 'MOD09A1_Point_2020_b1_b7_scaled',
fileFormat: 'CSV'
});
(2)工具准备
Matlab:用于编写代码,执行LAI反演全过程。
ArcMap:用于反演过程中查看出来的结果,对比不同数据源的LAI值。
4 反演方法
(1)反演过程
本次实习主要采用基于PROSAIL物理模型的贝叶斯反演方法从MODIS地表反射率数据中反演叶面积指数(LAI)。
Step1:从2000-2020年MOD15A2H产品中提取同区域的LAI数据,计算多年平均值作为先验信息,建立误差协方差矩阵B。
Step2:构建贝叶斯代价函数:
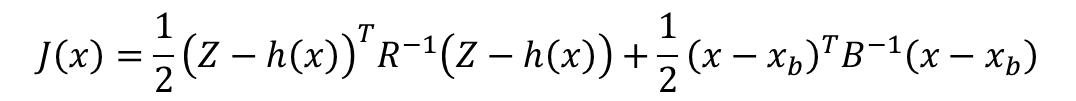
这里我使用了Matlab编写代价函数,方便进行调用。
function cost = functn(nopt, x)
%% ========================================================================
% 贝叶斯代价函数 - 用于LAI反演
%
% 输入:
% nopt - 参数维度 (此处为1, 即LAI)
% x - 当前LAI值
%
% 输出:
% cost - 代价函数值
%
% 代价函数形式:
% J(x) = 0.5 * (z - h(x))' * R^(-1) * (z - h(x)) +
% 0.5 * (x - x_b)' * B^(-1) * (x - x_b)
%
% 其中:
% z: 观测反射率
% h(x): PROSAIL模型模拟的反射率
% R: 观测误差协方差矩阵
% x_b: 先验LAI均值
% B: 背景误差协方差
% ========================================================================
global CURRENT_OBS CURRENT_PRIOR FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL WEIGHT_OBS WEIGHT_PRIOR
% 参数有效性检查
if x <= 0 || x > 10
cost = 1e10;
return;
end
try
%% ====================================================================
% 1. 运行PROSAIL模型
% ====================================================================
% 加载光谱数据
data = dataSpec_P5B;
% 土壤反射率
Rsoil1 = data(:, 10); % 干土壤
Rsoil2 = data(:, 11); % 湿土壤
rsoil0 = FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.psoil * Rsoil1 + ...
(1 - FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.psoil) * Rsoil2;
% 运行PRO4SAIL模型
[rdot, rsot, rddt, rsdt] = PRO4SAIL(...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.N, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.Cab, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.Car, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.Cbrown, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.Cw, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.Cm, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.LIDFa, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.LIDFb, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.TypeLidf, ...
x, ... % LAI
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.hspot, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.tts, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.tto, ...
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.psi, ...
rsoil0);
% 计算天空光比例
rd = pi / 180;
skyl = 0.847 - 1.61 * sin((90 - FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.tts) * rd) + ...
1.04 * sin((90 - FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL.tts) * rd)^2;
% 直射和漫射光
Es = data(:, 8);
Ed = data(:, 9);
PARdiro = (1 - skyl) * Es;
PARdifo = skyl * Ed;
% 计算方向反射率
resv = (rdot .* PARdifo + rsot .* PARdiro) ./ (PARdiro + PARdifo);
%% ====================================================================
% 2. 提取对应MODIS波段的模拟反射率
% ====================================================================
% MODIS波段中心波长 (nm)
modis_bands = [645, 858.5, 469, 555, 1240, 1640, 2130];
wavelengths = data(:, 1);
% 提取7个MODIS波段的模拟反射率
simulated_ref = zeros(7, 1);
for i = 1:7
[~, idx] = min(abs(wavelengths - modis_bands(i)));
simulated_ref(i) = resv(idx);
end
%% ====================================================================
% 3. 计算观测项 (Observation Term)
% ====================================================================
% 观测误差标准差 (假设为反射率的5%)
obs_error_std = 0.05;
% 计算残差
residual = CURRENT_OBS - simulated_ref;
% 观测项代价 (假设R为对角矩阵)
cost_obs = 0.5 * sum((residual / obs_error_std).^2);
%% ====================================================================
% 4. 计算先验项 (Prior Term)
% ====================================================================
% 先验误差标准差 (LAI的标准差,假设为1.0)
prior_error_std = 1.0;
% 先验项代价
cost_prior = 0.5 * ((x - CURRENT_PRIOR) / prior_error_std)^2;
%% ====================================================================
% 5. 总代价函数
% ====================================================================
cost = WEIGHT_OBS * cost_obs + WEIGHT_PRIOR * cost_prior;
% 检查cost是否为有限数
if ~isfinite(cost)
cost = 1e10;
end
catch ME
% 如果发生错误,返回一个大的代价值
cost = 1e10;
end
end
式子中,第一项为观测项,第二项是先验项,其中Z是观测反射率,h(x)是ProSAIL模型模拟的反射率。代价函数的构建通过编写matlab函数实现。
Step3:采用SCEUA(Shuffled Complex Evolution - University of Arizona)全局优化算法最小化代价函数,反演得到LAI结果。
SCE-UA算法的实现函数:
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [bestx,bestf] = sceua(x0,bl,bu,maxn,kstop,pcento,peps,ngs,iseed,iniflg)
% This is the subroutine implementing the SCE algorithm,
% written by Q.Duan, 9/2004
%
% Definition:
% x0 = the initial parameter array at the start;
% = the optimized parameter array at the end;
% f0 = the objective function value corresponding to the initial parameters
% = the objective function value corresponding to the optimized parameters
% bl = the lower bound of the parameters
% bu = the upper bound of the parameters
% iseed = the random seed number (for repetetive testing purpose)
% iniflg = flag for initial parameter array (=1, included it in initial
% population; otherwise, not included)
% ngs = number of complexes (sub-populations)
% npg = number of members in a complex
% nps = number of members in a simplex
% nspl = number of evolution steps for each complex before shuffling
% mings = minimum number of complexes required during the optimization process
% maxn = maximum number of function evaluations allowed during optimization
% kstop = maximum number of evolution loops before convergency
% percento = the percentage change allowed in kstop loops before convergency
% LIST OF LOCAL VARIABLES
% x(.,.) = coordinates of points in the population
% xf(.) = function values of x(.,.)
% xx(.) = coordinates of a single point in x
% cx(.,.) = coordinates of points in a complex
% cf(.) = function values of cx(.,.)
% s(.,.) = coordinates of points in the current simplex
% sf(.) = function values of s(.,.)
% bestx(.) = best point at current shuffling loop
% bestf = function value of bestx(.)
% worstx(.) = worst point at current shuffling loop
% worstf = function value of worstx(.)
% xnstd(.) = standard deviation of parameters in the population
% gnrng = normalized geometri%mean of parameter ranges
% lcs(.) = indices locating position of s(.,.) in x(.,.)
% bound(.) = bound on ith variable being optimized
% ngs1 = number of complexes in current population
% ngs2 = number of complexes in last population
% iseed1 = current random seed
% criter(.) = vector containing the best criterion values of the last
% 10 shuffling loops
global BESTX BESTF ICALL PX PF
% Initialize SCE parameters:
nopt=length(x0);
npg=2*nopt+1;
nps=nopt+1;
nspl=npg;
mings=ngs;
npt=npg*ngs;
bound = bu-bl;
% Create an initial population to fill array x(npt,nopt):
rand('seed',iseed);
x=zeros(npt,nopt);
for i=1:npt;
x(i,:)=bl+rand(1,nopt).*bound;
end;
if iniflg==1; x(1,:)=x0; end;
nloop=0;
icall=0;
for i=1:npt;
xf(i) = functn(nopt,x(i,:));
icall = icall + 1;
end;
f0=xf(1);
% Sort the population in order of increasing function values;
[xf,idx]=sort(xf);
x=x(idx,:);
% Record the best and worst points;
bestx=x(1,:); bestf=xf(1);
worstx=x(npt,:); worstf=xf(npt);
BESTF=bestf; BESTX=bestx;ICALL=icall;
% Compute the standard deviation for each parameter
xnstd=std(x);
% Computes the normalized geometric range of the parameters
gnrng=exp(mean(log((max(x)-min(x))./bound)));
disp('The Initial Loop: 0');
disp(['BESTF : ' num2str(bestf)]);
disp(['BESTX : ' num2str(bestx)]);
disp(['WORSTF : ' num2str(worstf)]);
disp(['WORSTX : ' num2str(worstx)]);
disp(' ');
% Check for convergency;
if icall >= maxn;
disp('*** OPTIMIZATION SEARCH TERMINATED BECAUSE THE LIMIT');
disp('ON THE MAXIMUM NUMBER OF TRIALS ');
disp(maxn);
disp('HAS BEEN EXCEEDED. SEARCH WAS STOPPED AT TRIAL NUMBER:');
disp(icall);
disp('OF THE INITIAL LOOP!');
end;
if gnrng < peps;
disp('THE POPULATION HAS CONVERGED TO A PRESPECIFIED SMALL PARAMETER SPACE');
end;
% Begin evolution loops:
nloop = 0;
criter=[];
criter_change=1e+5;
while icallpeps & criter_change>pcento;
nloop=nloop+1;
% Loop on complexes (sub-populations);
for igs = 1: ngs;
% Partition the population into complexes (sub-populations);
k1=1:npg;
k2=(k1-1)*ngs+igs;
cx(k1,:) = x(k2,:);
cf(k1) = xf(k2);
% Evolve sub-population igs for nspl steps:
for loop=1:nspl;
% Select simplex by sampling the complex according to a linear
% probability distribution
lcs(1) = 1;
for k3=2:nps;
for iter=1:1000;
lpos = 1 + floor(npg+0.5-sqrt((npg+0.5)^2 - npg*(npg+1)*rand));
idx=find(lcs(1:k3-1)==lpos); if isempty(idx); break; end;
end;
lcs(k3) = lpos;
end;
lcs=sort(lcs);
% Construct the simplex:
s = zeros(nps,nopt);
s=cx(lcs,:); sf = cf(lcs);
[snew,fnew,icall]=cceua(s,sf,bl,bu,icall,maxn);
% Replace the worst point in Simplex with the new point:
s(nps,:) = snew; sf(nps) = fnew;
% Replace the simplex into the complex;
cx(lcs,:) = s;
cf(lcs) = sf;
% Sort the complex;
[cf,idx] = sort(cf); cx=cx(idx,:);
% End of Inner Loop for Competitive Evolution of Simplexes
end;
% Replace the complex back into the population;
x(k2,:) = cx(k1,:);
xf(k2) = cf(k1);
% End of Loop on Complex Evolution;
end;
% Shuffled the complexes;
[xf,idx] = sort(xf); x=x(idx,:);
PX=x; PF=xf;
% Record the best and worst points;
bestx=x(1,:); bestf=xf(1);
worstx=x(npt,:); worstf=xf(npt);
BESTX=[BESTX;bestx]; BESTF=[BESTF;bestf];ICALL=[ICALL;icall];
% Compute the standard deviation for each parameter
xnstd=std(x);
% Computes the normalized geometric range of the parameters
gnrng=exp(mean(log((max(x)-min(x))./bound)));
disp(['Evolution Loop: ' num2str(nloop) ' - Trial - ' num2str(icall)]);
disp(['BESTF : ' num2str(bestf)]);
disp(['BESTX : ' num2str(bestx)]);
disp(['WORSTF : ' num2str(worstf)]);
disp(['WORSTX : ' num2str(worstx)]);
disp(' ');
% Check for convergency;
if icall >= maxn;
disp('*** OPTIMIZATION SEARCH TERMINATED BECAUSE THE LIMIT');
disp(['ON THE MAXIMUM NUMBER OF TRIALS ' num2str(maxn) ' HAS BEEN EXCEEDED!']);
end;
if gnrng < peps;
disp('THE POPULATION HAS CONVERGED TO A PRESPECIFIED SMALL PARAMETER SPACE');
end;
criter=[criter;bestf];
if (nloop >= kstop);
criter_change=abs(criter(nloop)-criter(nloop-kstop+1))*100;
criter_change=criter_change/mean(abs(criter(nloop-kstop+1:nloop)));
if criter_change < pcento;
disp(['THE BEST POINT HAS IMPROVED IN LAST ' num2str(kstop) ' LOOPS BY ', ...
'LESS THAN THE THRESHOLD ' num2str(pcento) '%']);
disp('CONVERGENCY HAS ACHIEVED BASED ON OBJECTIVE FUNCTION CRITERIA!!!')
end;
end;
% End of the Outer Loops
end;
disp(['SEARCH WAS STOPPED AT TRIAL NUMBER: ' num2str(icall)]);
disp(['NORMALIZED GEOMETRIC RANGE = ' num2str(gnrng)]);
disp(['THE BEST POINT HAS IMPROVED IN LAST ' num2str(kstop) ' LOOPS BY ', ...
num2str(criter_change) '%']);
% END of Subroutine sceua
return;
与之配套的还需要CCEUA函数,代码如下:
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [snew,fnew,icall]=cceua(s,sf,bl,bu,icall,maxn)
% This is the subroutine for generating a new point in a simplex
%
% s(.,.) = the sorted simplex in order of increasing function values
% s(.) = function values in increasing order
%
% LIST OF LOCAL VARIABLES
% sb(.) = the best point of the simplex
% sw(.) = the worst point of the simplex
% w2(.) = the second worst point of the simplex
% fw = function value of the worst point
% ce(.) = the centroid of the simplex excluding wo
% snew(.) = new point generated from the simplex
% iviol = flag indicating if constraints are violated
% = 1 , yes
% = 0 , no
[nps,nopt]=size(s);
n = nps;
m = nopt;
alpha = 1.0;
beta = 0.5;
% Assign the best and worst points:
sb=s(1,:); fb=sf(1);
sw=s(n,:); fw=sf(n);
% Compute the centroid of the simplex excluding the worst point:
ce=mean(s(1:n-1,:));
% Attempt a reflection point
snew = ce + alpha*(ce-sw);
% Check if is outside the bounds:
ibound=0;
s1=snew-bl; idx=find(s1<0); if ~isempty(idx); ibound=1; end;
s1=bu-snew; idx=find(s1<0); if ~isempty(idx); ibound=2; end;
if ibound >=1;
snew = bl + rand(1,nopt).*(bu-bl);
end;
fnew = functn(nopt,snew);
icall = icall + 1;
% Reflection failed; now attempt a contraction point:
if fnew > fw;
snew = sw + beta*(ce-sw);
fnew = functn(nopt,snew);
icall = icall + 1;
% Both reflection and contraction have failed, attempt a random point;
if fnew > fw;
snew = bl + rand(1,nopt).*(bu-bl);
fnew = functn(nopt,snew);
icall = icall + 1;
end;
end;
% END OF CCE
return;
其中PROSAIL模型耦合了PROSPECT-5B叶片光学模型和4SAIL冠层辐射传输模型,通过迭代优化使模拟的7个MODIS波段反射率与观测值拟合,并受先验信息约束以提高反演稳定性和精度。
Step4:输出的反演LAI结果,和地面站点以及同日期的MODIS的LAI数据进行对比,计算反演结果的精度,此处主要采用散点图的形式进行。
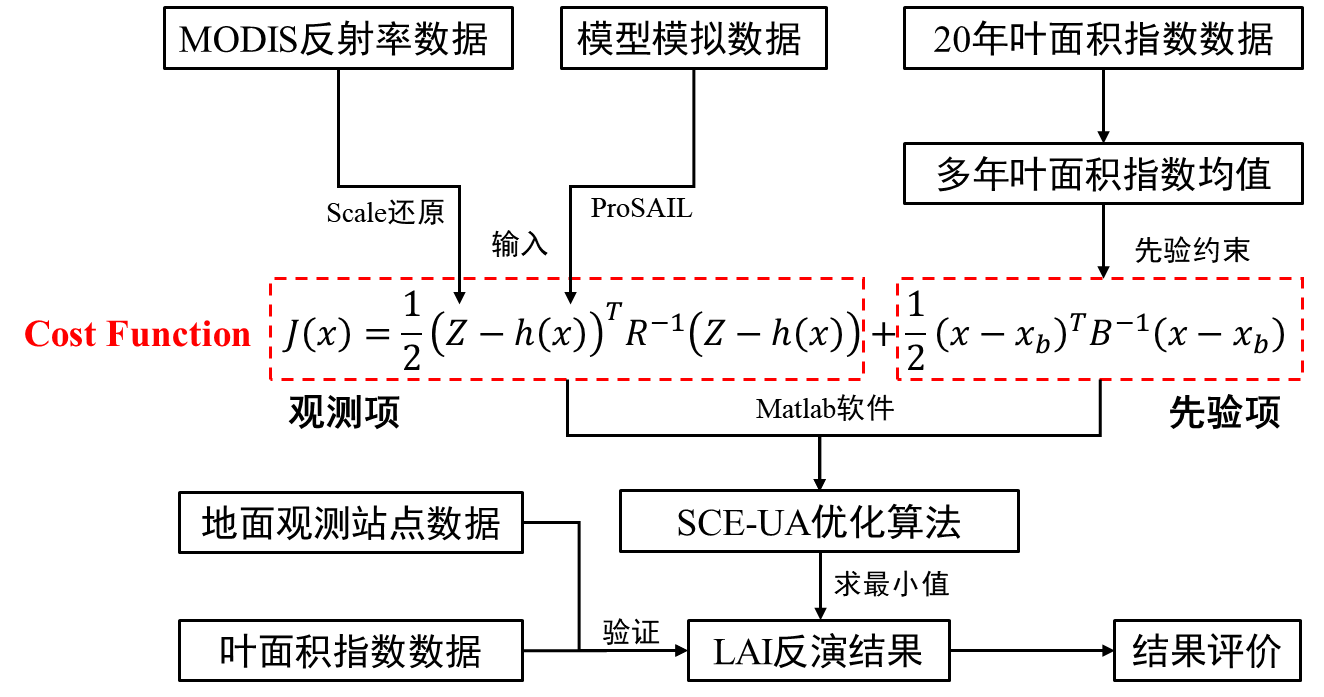
图 基于物理模型的LAI反演框架
站点所在像元一年的LAI反演的方式与上面类似,只是将空间上的逐像元反演转化为单个像元在时间序列上的反演。只需获取像元点的MODIS波段反射率数据即可。
(2)ProSAIL模型介绍
本次实习用到的模型为PROSAIL模型,综合课程讲解和文献资料,现对模型介绍如下:
随着光学遥感技术的发展,辐射传输模型致力于理解植物冠层对光的截获,并根据生物物理特征解释植被反射率。PROSAIL模型便是一种经典的辐射传输模型,由PROSPECT叶片光学特性模型和 SAILH 冠层结构模型耦合得到,目前已被广泛用于研究太阳辐射域内植物冠层的光谱和方向反射率,以及生物物理化学参数反演等研究。
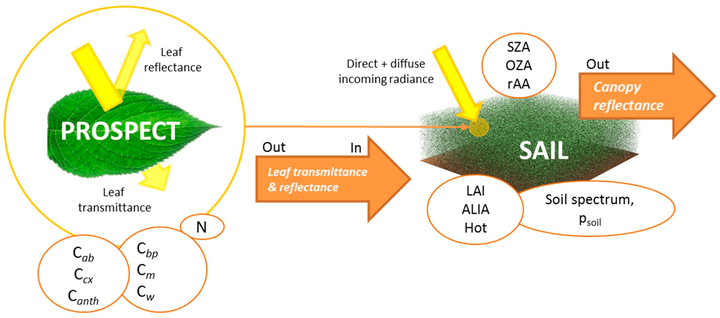
图 PROSAIL模型参数示意图
ProSAIL模型模拟的过程采用ProSAI_5B包进行,需要从其他渠道获取,如您有需要,也可以私信小编进行获取。
(3)SCE-UA算法介绍
SCE-UA算法由美国亚利桑那州大学水文与水资源系的Qingyun Duan博士提出。它的基本原理是通过把参数空间里的种群分成若干个子群,每个子群内部用单纯形的操作沿着下降方向搜索,从而在局部快速逼近更优解。SCE-UA综合了确定性搜索、随机搜索和生物竞争进化等方法的优点, 引入种群概念, 复合形点在可行域内随机生成和竞争演化[2-4]。
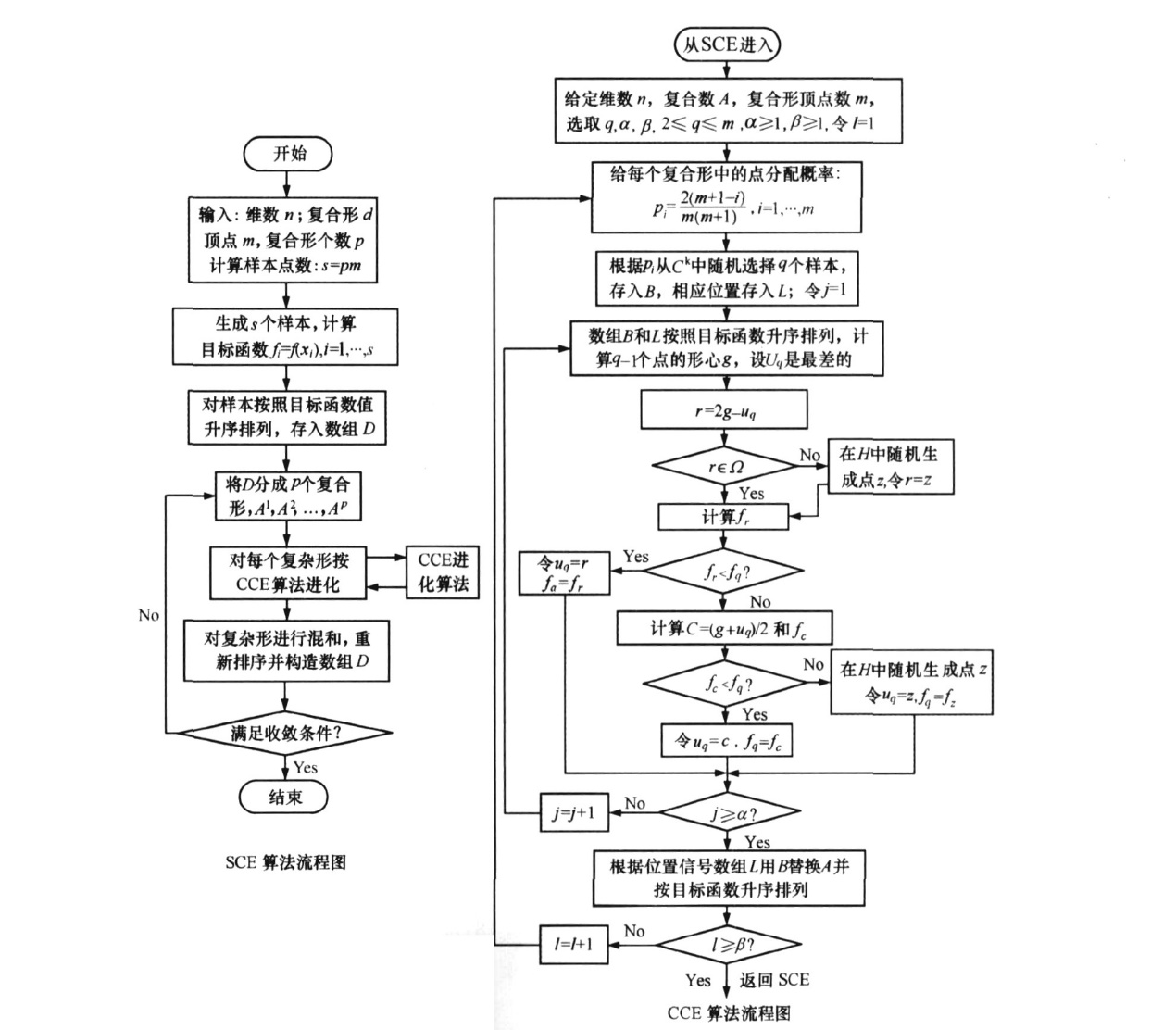
图 SCE-UA算法流程图(宋星原等,2009)
SCE-UA算法的实现过程主要通过老师分享的代码包来实现,通过调用编写的代价函数,执行迭代过程。站点小区域的主程序如下:
%% ========================================================================
% 草地LAI反演 - 标准贝叶斯公式 + SCE-UA算法 - 完整版
%
% 代价函数: J(x) = 1/2*(z-h(x))'*R^(-1)*(z-h(x)) + 1/2*(x-x_b)'*B^(-1)*(x-x_b)
% 优化算法: SCE-UA (Shuffled Complex Evolution)
% 站点: Wankama 2005草地
%% ========================================================================
clear; clc; close all;
fprintf('================================================================
');
fprintf(' 草地LAI反演 - 标准贝叶斯公式 + SCE-UA算法
');
fprintf('================================================================
');
fprintf('站点: Wankama 2005
');
fprintf('日期: 2005-06-27
');
fprintf('================================================================
');
addpath('D:Duyan
emote_sensingLAIGrasslandGrassland_LAI_Inversion_PackageGrassland_LAI_Inversion_Package');
%% ========================================================================
% 1. 数据路径设置
%% ========================================================================
data_dir = 'D:Duyan
emote_sensingLAIGrasslandGEE_MODIS';
date_str = '20050627';
ref_files = cell(7,1);
for i = 1:7
ref_files{i} = fullfile(data_dir, sprintf('MOD09A1_near_%s_ROI5km_b%d.tif', date_str, i));
end
modis_lai_file = fullfile(data_dir, sprintf('MOD15A2H_LAI_near_%s_ROI5km.tif', date_str));
prior_lai_file = fullfile(data_dir, 'MOD15A2H_LAI_priorMean_2002_2025_near_0627_ROI5km.tif');
ground_data_file = fullfile(data_dir, 'Wankama2005GroundData_latlon.xlsx');
output_dir = 'D:Duyan
emote_sensingLAIGrasslandGrassland_LAI_Inversion_PackageGrassland_LAI_Inversion_Packageoutputs';
if ~exist(output_dir, 'dir'), mkdir(output_dir); end
%% ========================================================================
% 2. 读取遥感数据
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
正在读取数据...
');
[ref_b1, R] = readgeoraster(ref_files{1});
[nrows, ncols] = size(ref_b1);
fprintf('影像尺寸: %d x %d
', nrows, ncols);
reflectance = zeros(nrows, ncols, 7);
for i = 1:7
reflectance(:,:,i) = readgeoraster(ref_files{i});
fprintf(' 波段%d读取完成
', i);
end
modis_lai = readgeoraster(modis_lai_file);
prior_lai_mean = readgeoraster(prior_lai_file);
% 处理无效值
reflectance(reflectance < 0 | reflectance > 1) = NaN;
modis_lai(modis_lai < 0 | modis_lai > 10) = NaN;
prior_lai_mean(prior_lai_mean < 0 | prior_lai_mean > 10) = NaN;
% 先验LAI统计
prior_valid = prior_lai_mean(~isnan(prior_lai_mean) & prior_lai_mean > 0);
fprintf('
先验LAI统计:
');
fprintf(' 范围: [%.6f, %.6f]
', min(prior_valid), max(prior_valid));
fprintf(' 均值: %.6f ± %.6f
', mean(prior_valid), std(prior_valid));
%% ========================================================================
% 3. 读取地面观测数据
%% ========================================================================
try
ground_data = readtable(ground_data_file);
fprintf('
地面观测样点: %d
', height(ground_data));
catch
fprintf('
警告: 无法读取地面数据
');
ground_data = [];
end
%% ========================================================================
% 4. 贝叶斯参数设置
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
================================================================
');
fprintf(' 贝叶斯反演参数设置
');
fprintf('================================================================
');
% PROSAIL模型参数 (草地)
fixed_params = struct();
fixed_params.N = 1.3;
fixed_params.Cab = 35;
fixed_params.Car = 9;
fixed_params.Cbrown = 0.0;
fixed_params.Cw = 0.010;
fixed_params.Cm = 0.004;
fixed_params.psoil = 0.4;
fixed_params.LIDFa = 70;
fixed_params.LIDFb = 0;
fixed_params.TypeLidf = 2;
fixed_params.hspot = 0.01;
fixed_params.tts = 30;
fixed_params.tto = 10;
fixed_params.psi = 0;
fprintf('
PROSAIL参数 (草地):
');
fprintf(' N=%.1f, Cab=%d, Cw=%.3f, LIDFa=%d°
', ...
fixed_params.N, fixed_params.Cab, fixed_params.Cw, fixed_params.LIDFa);
% 协方差矩阵设置
obs_error_std = 0.03;
R_matrix = (obs_error_std^2) * eye(7);
prior_error_std = 0.5;
B_variance = prior_error_std^2;
fprintf('
协方差矩阵:
');
fprintf(' R: 观测误差协方差 (对角,标准差=%.3f)
', obs_error_std);
fprintf(' B: 背景误差方差 (%.4f)
', B_variance);
% LAI范围
lai_min = max(0.05, min(prior_valid) - 0.15);
lai_max = min(5.0, max(prior_valid) + 1.0);
fprintf('
LAI反演范围: [%.4f, %.4f]
', lai_min, lai_max);
% SCE-UA参数
sce_params = struct();
sce_params.maxn = 10000;
sce_params.kstop = 15;
sce_params.pcento = 0.01;
sce_params.peps = 0.001;
sce_params.ngs = 5;
sce_params.iseed = 123;
sce_params.iniflg = 1;
fprintf('
SCE-UA参数: maxn=%d, pcento=%.2f%%
', sce_params.maxn, sce_params.pcento);
%% ========================================================================
% 5. 逐像元LAI反演
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
================================================================
');
fprintf(' 开始逐像元LAI反演 (SCE-UA)
');
fprintf('================================================================
');
inverted_lai = nan(nrows, ncols);
convergence_flag = zeros(nrows, ncols);
cost_values = nan(nrows, ncols);
valid_pixels = 0;
total_pixels = nrows * ncols;
global CURRENT_OBS CURRENT_PRIOR FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL ...
OBS_COV_MATRIX PRIOR_VARIANCE
FIXED_PARAMS_GLOBAL = fixed_params;
OBS_COV_MATRIX = R_matrix;
PRIOR_VARIANCE = B_variance;
tic;
for i = 1:nrows
for j = 1:ncols
if mod((i-1)*ncols + j, 20) == 0
fprintf(' 进度: %d/%d (%.1f%%)
', (i-1)*ncols+j, total_pixels, ...
((i-1)*ncols+j)/total_pixels*100);
end
pixel_ref = squeeze(reflectance(i, j, :));
if any(isnan(pixel_ref)) || all(pixel_ref == 0) || any(pixel_ref < 0.001)
continue;
end
prior_lai_pixel = prior_lai_mean(i, j);
if isnan(prior_lai_pixel) || prior_lai_pixel <= 0
prior_lai_pixel = mean(prior_valid);
end
CURRENT_OBS = pixel_ref;
CURRENT_PRIOR = prior_lai_pixel;
lai_init = prior_lai_pixel;
try
[best_lai, best_cost, exitflag] = sceua(@functn, ...
lai_init, lai_min, lai_max, ...
sce_params.maxn, sce_params.kstop, ...
sce_params.pcento, sce_params.peps, ...
sce_params.ngs, sce_params.iseed, ...
sce_params.iniflg);
if isnan(best_lai) || isinf(best_cost) || best_cost > 1e10
best_lai = prior_lai_pixel;
exitflag = -1;
end
best_lai = max(lai_min, min(lai_max, best_lai));
inverted_lai(i, j) = best_lai;
cost_values(i, j) = best_cost;
convergence_flag(i, j) = (exitflag >= 0);
valid_pixels = valid_pixels + 1;
catch
inverted_lai(i, j) = prior_lai_pixel;
end
end
end
elapsed_time = toc;
fprintf('
反演完成! 用时: %.1f分钟
', elapsed_time/60);
fprintf(' 有效像元: %d/%d (%.1f%%)
', valid_pixels, total_pixels, ...
valid_pixels/total_pixels*100);
valid_lai = inverted_lai(~isnan(inverted_lai) & inverted_lai > 0);
fprintf('
反演LAI统计:
');
fprintf(' 范围: [%.6f, %.6f]
', min(valid_lai), max(valid_lai));
fprintf(' 均值: %.6f ± %.6f
', mean(valid_lai), std(valid_lai));
converged = sum(convergence_flag(:));
fprintf('
收敛率: %.1f%%
', converged/valid_pixels*100);
%% ========================================================================
% 6. 保存结果
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
正在保存结果...
');
geotiffwrite(fullfile(output_dir, sprintf('Grassland_Bayesian_LAI_%s.tif', date_str)), ...
inverted_lai, R);
geotiffwrite(fullfile(output_dir, sprintf('Grassland_Bayesian_Cost_%s.tif', date_str)), ...
cost_values, R);
geotiffwrite(fullfile(output_dir, sprintf('Grassland_Bayesian_Convergence_%s.tif', date_str)), ...
convergence_flag, R);
%% ========================================================================
% 7. 生成所需图表
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
================================================================
');
fprintf(' 生成可视化图表
');
fprintf('================================================================
');
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
% 图1: 四张LAI对比图 (反演、MODIS、先验、差值)
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
fprintf(' 生成图1: LAI对比图...
');
figure('Position', [100, 100, 1800, 900]);
% 子图1: 反演LAI
subplot(2,2,1);
imagesc(inverted_lai);
h1 = colorbar;
ylabel(h1, 'LAI', 'FontSize', 10);
inv_min = min(valid_lai); inv_max = max(valid_lai);
caxis([inv_min*0.95 inv_max*1.05]);
title(sprintf('反演LAI (贝叶斯+SCE-UA)
范围: [%.4f, %.4f]', inv_min, inv_max), ...
'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
axis image;
colormap(jet);
xlabel(sprintf('均值: %.4f, 标准差: %.4f', mean(valid_lai), std(valid_lai)), ...
'FontSize', 10);
% 子图2: MODIS LAI
subplot(2,2,2);
imagesc(modis_lai);
h2 = colorbar;
ylabel(h2, 'LAI', 'FontSize', 10);
modis_valid = modis_lai(~isnan(modis_lai) & modis_lai > 0);
modis_min = min(modis_valid); modis_max = max(modis_valid);
caxis([modis_min*0.95 modis_max*1.05]);
title(sprintf('MODIS LAI产品
范围: [%.4f, %.4f]', modis_min, modis_max), ...
'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
axis image;
colormap(jet);
xlabel(sprintf('均值: %.4f, 标准差: %.4f', mean(modis_valid), std(modis_valid)), ...
'FontSize', 10);
% 子图3: 先验LAI (多年均值)
subplot(2,2,3);
imagesc(prior_lai_mean);
h3 = colorbar;
ylabel(h3, 'LAI', 'FontSize', 10);
prior_min = min(prior_valid); prior_max = max(prior_valid);
caxis([prior_min*0.95 prior_max*1.05]);
title(sprintf('先验LAI (多年均值 2002-2025)
范围: [%.6f, %.6f]', prior_min, prior_max), ...
'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
axis image;
colormap(jet);
xlabel(sprintf('均值: %.6f, 标准差: %.6f', mean(prior_valid), std(prior_valid)), ...
'FontSize', 10);
% 子图4: 差值图 (反演 - MODIS)
subplot(2,2,4);
diff_lai = inverted_lai - modis_lai;
imagesc(diff_lai);
h4 = colorbar;
ylabel(h4, 'LAI差值', 'FontSize', 10);
diff_valid = diff_lai(~isnan(diff_lai));
diff_abs_max = max(abs(diff_valid));
caxis([-diff_abs_max diff_abs_max]);
title(sprintf('差值图 (反演LAI - MODIS LAI)
范围: [%.4f, %.4f]', ...
min(diff_valid), max(diff_valid)), ...
'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
axis image;
colormap(gca, redblue);
xlabel(sprintf('均值: %.4f, 标准差: %.4f', mean(diff_valid), std(diff_valid)), ...
'FontSize', 10);
sgtitle('草地LAI反演结果对比 (标准贝叶斯公式+SCE-UA)', ...
'FontSize', 14, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
saveas(gcf, fullfile(output_dir, 'Grassland_Bayesian_LAI_Comparison.png'));
fprintf(' 已保存: Grassland_Bayesian_LAI_Comparison.png
');
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
% 图2: 反演LAI直方图
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
fprintf(' 生成图2: 反演LAI直方图...
');
figure('Position', [100, 100, 900, 700]);
histogram(valid_lai, 30, 'FaceColor', [0.2 0.6 0.8], 'EdgeColor', 'black');
hold on;
% 添加统计线
xline(mean(valid_lai), 'r--', 'LineWidth', 2, 'Label', sprintf('均值: %.4f', mean(valid_lai)));
xline(median(valid_lai), 'g--', 'LineWidth', 2, 'Label', sprintf('中位数: %.4f', median(valid_lai)));
xlabel('LAI', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
ylabel('频数', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
title('反演LAI分布直方图', 'FontSize', 14, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
grid on;
% 添加统计信息文本框
dim = [0.15 0.7 0.3 0.2];
str = {sprintf('样本数: %d', length(valid_lai)), ...
sprintf('范围: [%.4f, %.4f]', min(valid_lai), max(valid_lai)), ...
sprintf('均值: %.6f', mean(valid_lai)), ...
sprintf('标准差: %.6f', std(valid_lai)), ...
sprintf('中位数: %.6f', median(valid_lai)), ...
sprintf('四分位距: %.6f', iqr(valid_lai))};
annotation('textbox', dim, 'String', str, 'FitBoxToText', 'on', ...
'BackgroundColor', 'white', 'EdgeColor', 'black', 'FontSize', 10);
saveas(gcf, fullfile(output_dir, 'Grassland_Bayesian_LAI_Histogram.png'));
fprintf(' 已保存: Grassland_Bayesian_LAI_Histogram.png
');
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
% 图3: 散点图1 - 反演LAI vs MODIS LAI
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
fprintf(' 生成图3: 反演LAI vs MODIS LAI散点图...
');
valid_mask = ~isnan(inverted_lai) & ~isnan(modis_lai) & ...
inverted_lai > 0 & modis_lai > 0;
inv_lai_vec = inverted_lai(valid_mask);
modis_lai_vec = modis_lai(valid_mask);
figure('Position', [100, 100, 900, 700]);
scatter(modis_lai_vec, inv_lai_vec, 35, 'filled', 'MarkerFaceAlpha', 0.6);
hold on;
% 自适应坐标轴
all_lai = [inv_lai_vec; modis_lai_vec];
axis_min = max(0, min(all_lai) * 0.90);
axis_max = max(all_lai) * 1.10;
% 1:1线
plot([axis_min axis_max], [axis_min axis_max], 'r--', 'LineWidth', 2.5);
% 线性拟合
p = polyfit(modis_lai_vec, inv_lai_vec, 1);
x_fit = linspace(axis_min, axis_max, 100);
y_fit = polyval(p, x_fit);
plot(x_fit, y_fit, 'b-', 'LineWidth', 2);
% 统计指标
rmse = sqrt(mean((inv_lai_vec - modis_lai_vec).^2));
bias = mean(inv_lai_vec - modis_lai_vec);
r = corrcoef(inv_lai_vec, modis_lai_vec);
r2 = r(1,2)^2;
mae = mean(abs(inv_lai_vec - modis_lai_vec));
xlabel('MODIS LAI', 'FontSize', 13, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
ylabel('反演LAI (贝叶斯+SCE-UA)', 'FontSize', 13, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
title('反演LAI vs MODIS LAI', 'FontSize', 14, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
grid on;
axis equal;
xlim([axis_min axis_max]);
ylim([axis_min axis_max]);
% 统计信息
text_x = axis_min + (axis_max - axis_min) * 0.05;
text_y = axis_max - (axis_max - axis_min) * 0.30;
text_str = sprintf(['R² = %.4f
' ...
'RMSE = %.6f
' ...
'MAE = %.6f
' ...
'Bias = %.6f
' ...
'y = %.3fx + %.3f
' ...
'N = %d'], ...
r2, rmse, mae, bias, p(1), p(2), length(inv_lai_vec));
text(text_x, text_y, text_str, 'FontSize', 11, ...
'BackgroundColor', 'white', 'EdgeColor', 'black', ...
'VerticalAlignment', 'top');
legend('数据点', '1:1线', '拟合线', 'Location', 'southeast', 'FontSize', 10);
saveas(gcf, fullfile(output_dir, 'Grassland_Bayesian_Scatter_MODIS.png'));
fprintf(' 已保存: Grassland_Bayesian_Scatter_MODIS.png
');
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
% 图4: 散点图2 - 反演LAI vs 地面观测LAI
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
if ~isempty(ground_data)
fprintf(' 生成图4: 反演LAI vs 地面观测LAI散点图...
');
% 确定LAI列
if ismember('LAItrue', ground_data.Properties.VariableNames)
ground_lai_col = 'LAItrue';
else
lai_cols = ground_data.Properties.VariableNames(...
contains(ground_data.Properties.VariableNames, 'LAI'));
if ~isempty(lai_cols)
ground_lai_col = lai_cols{1};
else
fprintf(' 警告: 未找到地面LAI列
');
ground_lai_col = '';
end
end
if ~isempty(ground_lai_col)
n_samples = height(ground_data);
ground_lai = ground_data.(ground_lai_col);
inv_lai_at_samples = zeros(n_samples, 1);
for k = 1:n_samples
lon = ground_data.Longitude(k);
lat = ground_data.Latitude(k);
[row, col] = geographicToDiscrete(R, lat, lon);
if row >= 1 && row <= nrows && col >= 1 && col <= ncols
inv_lai_at_samples(k) = inverted_lai(round(row), round(col));
else
inv_lai_at_samples(k) = NaN;
end
end
valid_samples = ~isnan(inv_lai_at_samples) & ~isnan(ground_lai) & ...
inv_lai_at_samples > 0 & ground_lai > 0;
inv_lai_samples = inv_lai_at_samples(valid_samples);
ground_lai_valid = ground_lai(valid_samples);
if sum(valid_samples) > 3
figure('Position', [100, 100, 900, 700]);
scatter(ground_lai_valid, inv_lai_samples, 100, 'filled', ...
'MarkerFaceAlpha', 0.7, 'MarkerEdgeColor', 'black');
hold on;
% 自适应坐标轴
all_lai_g = [inv_lai_samples; ground_lai_valid];
g_axis_min = max(0, min(all_lai_g) * 0.85);
g_axis_max = max(all_lai_g) * 1.15;
% 1:1线
plot([g_axis_min g_axis_max], [g_axis_min g_axis_max], ...
'r--', 'LineWidth', 2.5);
% 线性拟合
p_g = polyfit(ground_lai_valid, inv_lai_samples, 1);
x_fit_g = linspace(g_axis_min, g_axis_max, 100);
y_fit_g = polyval(p_g, x_fit_g);
plot(x_fit_g, y_fit_g, 'b-', 'LineWidth', 2);
% 统计指标
rmse_g = sqrt(mean((inv_lai_samples - ground_lai_valid).^2));
bias_g = mean(inv_lai_samples - ground_lai_valid);
r_g = corrcoef(inv_lai_samples, ground_lai_valid);
r2_g = r_g(1,2)^2;
mae_g = mean(abs(inv_lai_samples - ground_lai_valid));
xlabel('地面观测LAI', 'FontSize', 13, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
ylabel('反演LAI (贝叶斯+SCE-UA)', 'FontSize', 13, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
title('反演LAI vs 地面观测LAI', 'FontSize', 14, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
grid on;
axis equal;
xlim([g_axis_min g_axis_max]);
ylim([g_axis_min g_axis_max]);
% 统计信息
text_x_g = g_axis_min + (g_axis_max - g_axis_min) * 0.05;
text_y_g = g_axis_max - (g_axis_max - g_axis_min) * 0.35;
text_str_g = sprintf(['R² = %.4f
' ...
'RMSE = %.6f
' ...
'MAE = %.6f
' ...
'Bias = %.6f
' ...
'y = %.3fx + %.3f
' ...
'N = %d'], ...
r2_g, rmse_g, mae_g, bias_g, p_g(1), p_g(2), sum(valid_samples));
text(text_x_g, text_y_g, text_str_g, 'FontSize', 11, ...
'BackgroundColor', 'white', 'EdgeColor', 'black', ...
'VerticalAlignment', 'top');
legend('数据点', '1:1线', '拟合线', 'Location', 'southeast', 'FontSize', 10);
saveas(gcf, fullfile(output_dir, 'Grassland_Bayesian_Scatter_Ground.png'));
fprintf(' 已保存: Grassland_Bayesian_Scatter_Ground.png
');
fprintf('
与地面观测对比:
');
fprintf(' RMSE: %.6f
', rmse_g);
fprintf(' MAE: %.6f
', mae_g);
fprintf(' Bias: %.6f
', bias_g);
fprintf(' R²: %.6f
', r2_g);
end
end
else
fprintf(' 跳过图4: 无地面观测数据
');
end
%% ========================================================================
% 8. 保存统计报告
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
保存统计报告...
');
results_table = table();
results_table.Metric = {'Obs_Error_Std'; 'Prior_Error_Std'; ...
'RMSE_MODIS'; 'MAE_MODIS'; 'Bias_MODIS'; 'R2_MODIS'; ...
'Inv_LAI_Min'; 'Inv_LAI_Max'; 'Inv_LAI_Mean'; 'Inv_LAI_Std'; ...
'Prior_LAI_Min'; 'Prior_LAI_Max'; 'Prior_LAI_Mean'; 'Prior_LAI_Std'; ...
'Valid_Pixels'; 'Convergence_Rate'; 'Elapsed_Time_Min'};
results_table.Value = [obs_error_std; prior_error_std; ...
rmse; mae; bias; r2; ...
min(valid_lai); max(valid_lai); mean(valid_lai); std(valid_lai); ...
min(prior_valid); max(prior_valid); mean(prior_valid); std(prior_valid); ...
valid_pixels; converged/valid_pixels; elapsed_time/60];
writetable(results_table, fullfile(output_dir, 'Grassland_Bayesian_Statistics.csv'));
fprintf('
================================================================
');
fprintf(' 程序运行完成!
');
fprintf('================================================================
');
fprintf('算法: 标准贝叶斯公式 + SCE-UA
');
fprintf('反演LAI: [%.6f, %.6f], 均值=%.6f
', ...
min(valid_lai), max(valid_lai), mean(valid_lai));
fprintf('与MODIS对比: RMSE=%.6f, R²=%.6f
', rmse, r2);
fprintf('收敛率: %.1f%%
', converged/valid_pixels*100);
fprintf('用时: %.1f分钟
', elapsed_time/60);
fprintf('================================================================
');
fprintf('
生成的图表:
');
fprintf(' 1. Grassland_Bayesian_LAI_Comparison.png (4图对比)
');
fprintf(' 2. Grassland_Bayesian_LAI_Histogram.png (直方图)
');
fprintf(' 3. Grassland_Bayesian_Scatter_MODIS.png (vs MODIS)
');
fprintf(' 4. Grassland_Bayesian_Scatter_Ground.png (vs 地面)
');
fprintf('================================================================
');
% 辅助函数: 红蓝色图
function map = redblue(m)
if nargin < 1
m = size(get(gcf,'colormap'),1);
end
r = (0:m-1)'/max(m-1,1);
map = [max(0,1-2*r) ones(m,1)-2*abs(r-0.5) max(0,2*r-1)];
end
如果你需要反演某个像元一年的LAI的时间序列,可以使用如下的代码进行,二者还是比较类似的
%% ========================================================================
% LAI时间序列反演 - 单像元全年反演
%% ========================================================================
% 功能: 基于PROSAIL模型和SCE-UA优化算法反演单像元全年LAI时间序列
% 输入: MOD09A1反射率CSV + MOD15A2H LAI CSV
% 输出: 反演LAI时间序列 + 对比图表 + 精度统计
%
% 作者: Claude
% 日期: 2026-01-31
%% ========================================================================
clear; clc; close all;
fprintf('========================================
');
fprintf('LAI时间序列反演程序
');
fprintf('========================================
');
%% ========================================================================
% 1. 设置数据路径
%% ========================================================================
% 修改这里为你的数据路径
data_dir = 'D:Duyan
emote_sensingLAIForest';
% 输入文件
refl_file = fullfile(data_dir, 'MOD09A1_Point_2020_b1_b7_scaled.csv');
lai_file = fullfile(data_dir, 'MOD15A2H_LAI_Point_2020.csv');
% 输出目录
output_dir = fullfile(data_dir, 'output_timeseries');
if ~exist(output_dir, 'dir')
mkdir(output_dir);
end
fprintf('数据目录: %s
', data_dir);
fprintf('输出目录: %s
', output_dir);
%% ========================================================================
% 2. 读取时间序列数据
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
========================================
');
fprintf('读取时间序列数据
');
fprintf('========================================
');
% 读取反射率数据
fprintf('读取MOD09A1反射率数据...
');
refl_data = readtable(refl_file);
fprintf(' 时间点数: %d
', height(refl_data));
% 读取MODIS LAI数据
fprintf('读取MOD15A2H LAI数据...
');
lai_data = readtable(lai_file);
fprintf(' 时间点数: %d
', height(lai_data));
% 检查时间点数量是否一致
if height(refl_data) ~= height(lai_data)
warning('反射率和LAI数据时间点数量不一致!');
end
% 提取时间序列
n_times = height(refl_data);
dates = refl_data.system_index; % 时间列
% 提取7个波段反射率
b1 = refl_data.b1;
b2 = refl_data.b2;
b3 = refl_data.b3;
b4 = refl_data.b4;
b5 = refl_data.b5;
b6 = refl_data.b6;
b7 = refl_data.b7;
% 提取MODIS LAI
modis_lai = lai_data.LAI;
fprintf('数据读取完成!
');
fprintf(' 时间范围: %s 至 %s
', string(dates(1)), string(dates(end)));
fprintf(' MODIS LAI范围: %.2f - %.2f
', min(modis_lai), max(modis_lai));
%% ========================================================================
% 3. 设置PROSAIL模型固定参数
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
========================================
');
fprintf('设置PROSAIL模型参数
');
fprintf('========================================
');
% 叶片参数 (根据森林类型调整)
fixed_params.N = 1.5; % 叶片结构参数
fixed_params.Cab = 45; % 叶绿素含量 (μg/cm²) [30-60]
fixed_params.Car = 8; % 类胡萝卜素含量 (μg/cm²)
fixed_params.Cw = 0.015; % 等效水厚度 (cm) [0.01-0.03]
fixed_params.Cm = 0.005; % 干物质含量 (g/cm²)
fixed_params.Cbrown = 0; % 褐色素含量
% 冠层结构参数
fixed_params.LIDFa = 57; % 平均叶倾角 (度) [40-70]
fixed_params.TypeLidf = 2; % 叶倾角分布类型 (2=椭球分布)
fixed_params.lai = 3.0; % LAI初值 (将被优化)
% 土壤和背景
fixed_params.psoil = 1.0; % 土壤亮度系数
% 观测几何 (根据实际情况调整)
fixed_params.tts = 30; % 太阳天顶角 (度)
fixed_params.tto = 10; % 观测天顶角 (度)
fixed_params.psi = 0; % 相对方位角 (度)
fprintf('PROSAIL参数设置完成
');
fprintf(' 叶绿素: %.1f μg/cm²
', fixed_params.Cab);
fprintf(' 水分: %.4f cm
', fixed_params.Cw);
fprintf(' 平均叶倾角: %.1f°
', fixed_params.LIDFa);
%% ========================================================================
% 4. 设置SCE-UA优化参数
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
========================================
');
fprintf('设置优化算法参数
');
fprintf('========================================
');
% SCE-UA参数
sce_params.maxn = 5000; % 最大迭代次数 [3000-8000]
sce_params.kstop = 10; % 收敛判断次数
sce_params.pcento = 0.1; % 收敛阈值 (百分比)
sce_params.peps = 0.001; % 参数空间收敛阈值
sce_params.ngs = 5; % 复形数量 [3-7]
sce_params.iseed = 0; % 随机种子
sce_params.iniflg = 1; % 初始化标志
% LAI参数范围
lai_min = 0.1; % LAI最小值
lai_max = 7.0; % LAI最大值
fprintf('优化参数设置完成
');
fprintf(' 最大迭代: %d
', sce_params.maxn);
fprintf(' LAI范围: [%.1f, %.1f]
', lai_min, lai_max);
%% ========================================================================
% 5. 定义全局变量供代价函数使用
%% ========================================================================
global obs_refl fixed_prosail_params
%% ========================================================================
% 6. 时间序列反演循环
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
========================================
');
fprintf('开始时间序列反演
');
fprintf('========================================
');
% 初始化结果数组
inverted_lai = zeros(n_times, 1);
convergence_flag = zeros(n_times, 1);
iteration_count = zeros(n_times, 1);
% 记录开始时间
tic;
% 逐时间点反演
for t = 1:n_times
if mod(t, 5) == 0 || t == 1
fprintf('
处理时间点 %d/%d (%.1f%%)...
', t, n_times, 100*t/n_times);
end
% 提取当前时间点的7波段反射率
current_refl = [b1(t); b2(t); b3(t); b4(t); b5(t); b6(t); b7(t)];
% 检查数据有效性
if any(isnan(current_refl)) || any(current_refl < 0) || any(current_refl > 1)
fprintf(' 警告: 时间点%d数据无效,跳过
', t);
inverted_lai(t) = NaN;
convergence_flag(t) = -1;
continue;
end
% 设置全局变量
obs_refl = current_refl;
fixed_prosail_params = fixed_params;
% 初始LAI值
if t == 1
% 第一个时间点:使用MODIS LAI作为初值
x0 = modis_lai(t);
else
% 后续时间点:使用前一个反演结果作为初值
if ~isnan(inverted_lai(t-1)) && inverted_lai(t-1) > 0
x0 = inverted_lai(t-1);
else
x0 = modis_lai(t);
end
end
% 确保初值在范围内
x0 = max(lai_min, min(lai_max, x0));
% 调用SCE-UA优化算法
bl = lai_min; % 下界
bu = lai_max; % 上界
[bestx, bestf, icall, ~] = sceua(x0, bl, bu, sce_params.maxn, ...
sce_params.kstop, sce_params.pcento, sce_params.peps, ...
sce_params.ngs, sce_params.iseed, sce_params.iniflg);
% 保存结果
inverted_lai(t) = bestx;
iteration_count(t) = icall;
% 判断收敛
if bestf < 0.01 % 代价函数很小,认为收敛
convergence_flag(t) = 1;
else
convergence_flag(t) = 0;
fprintf(' 警告: 时间点%d未完全收敛 (代价函数=%.4f)
', t, bestf);
end
if mod(t, 5) == 0 || t == 1
fprintf(' 反演LAI: %.3f, MODIS LAI: %.3f, 迭代次数: %d
', ...
inverted_lai(t), modis_lai(t), icall);
end
end
% 记录结束时间
elapsed_time = toc;
fprintf('
========================================
');
fprintf('反演完成!
');
fprintf('========================================
');
fprintf('总耗时: %.1f 秒 (平均 %.2f 秒/点)
', elapsed_time, elapsed_time/n_times);
fprintf('收敛点数: %d/%d (%.1f%%)
', sum(convergence_flag==1), n_times, ...
100*sum(convergence_flag==1)/n_times);
fprintf('平均迭代次数: %.0f
', mean(iteration_count(convergence_flag==1)));
%% ========================================================================
% 7. 保存结果到CSV
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
========================================
');
fprintf('保存反演结果
');
fprintf('========================================
');
% 创建结果表格
results_table = table(dates, modis_lai, inverted_lai, convergence_flag, ...
'VariableNames', {'Date', 'MODIS_LAI', 'Inverted_LAI', 'Converged'});
% 保存为CSV
output_csv = fullfile(output_dir, 'LAI_TimeSeries_Results_2020.csv');
writetable(results_table, output_csv);
fprintf('结果已保存: %s
', output_csv);
%% ========================================================================
% 8. 精度验证
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
========================================
');
fprintf('精度验证统计
');
fprintf('========================================
');
% 仅使用收敛的点进行统计
valid_idx = (convergence_flag == 1) & ~isnan(inverted_lai) & ~isnan(modis_lai);
inv_valid = inverted_lai(valid_idx);
modis_valid = modis_lai(valid_idx);
if sum(valid_idx) < 3
warning('有效数据点太少,无法进行统计分析!');
else
% 计算精度指标
rmse = sqrt(mean((inv_valid - modis_valid).^2));
bias = mean(inv_valid - modis_valid);
mae = mean(abs(inv_valid - modis_valid));
% 计算R²
ss_res = sum((inv_valid - modis_valid).^2);
ss_tot = sum((modis_valid - mean(modis_valid)).^2);
r2 = 1 - ss_res/ss_tot;
% 显示统计结果
fprintf('有效样本数: %d
', sum(valid_idx));
fprintf('RMSE: %.4f
', rmse);
fprintf('Bias: %.4f
', bias);
fprintf('MAE: %.4f
', mae);
fprintf('R²: %.4f
', r2);
% 保存统计结果
stats_table = table({'RMSE'; 'Bias'; 'MAE'; 'R²'; 'Valid_Points'}, ...
[rmse; bias; mae; r2; sum(valid_idx)], ...
'VariableNames', {'Metric', 'Value'});
stats_csv = fullfile(output_dir, 'Validation_Statistics.csv');
writetable(stats_table, stats_csv);
fprintf('统计结果已保存: %s
', stats_csv);
end
%% ========================================================================
% 9. 绘制时间序列对比图
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
========================================
');
fprintf('生成可视化图表
');
fprintf('========================================
');
% 转换日期格式(如果可能)
try
date_nums = datenum(dates);
catch
date_nums = 1:n_times; % 如果日期转换失败,使用序号
end
% 图1: 时间序列对比图
figure('Position', [100, 100, 1200, 500]);
plot(date_nums, modis_lai, 'b-o', 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'MarkerSize', 6, ...
'DisplayName', 'MODIS LAI');
hold on;
plot(date_nums, inverted_lai, 'r-s', 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'MarkerSize', 6, ...
'DisplayName', 'Inverted LAI');
% 标记未收敛的点
unconverged_idx = (convergence_flag ~= 1);
if any(unconverged_idx)
plot(date_nums(unconverged_idx), inverted_lai(unconverged_idx), ...
'kx', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 2, 'DisplayName', 'Not Converged');
end
hold off;
xlabel('Date', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
ylabel('LAI', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
title('LAI Time Series Comparison - 2020', 'FontSize', 14, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
legend('Location', 'best', 'FontSize', 11);
grid on;
% 设置日期刻度(如果日期转换成功)
if exist('datenum', 'builtin')
datetick('x', 'mmm-yy', 'keepticks');
end
saveas(gcf, fullfile(output_dir, 'LAI_TimeSeries_Comparison.png'));
fprintf(' 时间序列图已保存
');
%% ========================================================================
% 10. 绘制散点图
%% ========================================================================
if sum(valid_idx) >= 3
figure('Position', [100, 100, 600, 600]);
scatter(modis_valid, inv_valid, 80, 'b', 'filled', 'MarkerEdgeColor', 'k');
hold on;
% 1:1线
min_val = min([modis_valid; inv_valid]);
max_val = max([modis_valid; inv_valid]);
plot([min_val, max_val], [min_val, max_val], 'k--', 'LineWidth', 1.5);
% 线性拟合
p = polyfit(modis_valid, inv_valid, 1);
fit_x = linspace(min_val, max_val, 100);
fit_y = polyval(p, fit_x);
plot(fit_x, fit_y, 'r-', 'LineWidth', 2);
hold off;
xlabel('MODIS LAI', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
ylabel('Inverted LAI', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
title('LAI Validation Scatter Plot', 'FontSize', 14, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
grid on;
axis equal;
xlim([min_val, max_val]);
ylim([min_val, max_val]);
% 添加统计信息
text_str = sprintf('R² = %.4f
RMSE = %.4f
Bias = %.4f
N = %d', ...
r2, rmse, bias, sum(valid_idx));
text(0.05, 0.95, text_str, 'Units', 'normalized', 'FontSize', 11, ...
'BackgroundColor', 'white', 'VerticalAlignment', 'top');
saveas(gcf, fullfile(output_dir, 'LAI_Scatter_Plot.png'));
fprintf(' 散点图已保存
');
end
%% ========================================================================
% 11. 绘制残差分析图
%% ========================================================================
if sum(valid_idx) >= 3
figure('Position', [100, 100, 1200, 400]);
% 残差
residuals = inv_valid - modis_valid;
subplot(1, 2, 1);
plot(date_nums(valid_idx), residuals, 'b-o', 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'MarkerSize', 6);
hold on;
yline(0, 'k--', 'LineWidth', 1.5);
yline(mean(residuals), 'r--', 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'DisplayName', ...
sprintf('Mean Bias = %.3f', bias));
hold off;
xlabel('Date', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
ylabel('Residual (Inverted - MODIS)', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
title('Residual Analysis', 'FontSize', 14, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
legend('Location', 'best');
grid on;
if exist('datenum', 'builtin')
datetick('x', 'mmm-yy', 'keepticks');
end
subplot(1, 2, 2);
histogram(residuals, 15, 'FaceColor', 'b', 'EdgeColor', 'k');
xlabel('Residual (Inverted - MODIS)', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
ylabel('Frequency', 'FontSize', 12, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
title('Residual Distribution', 'FontSize', 14, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
grid on;
saveas(gcf, fullfile(output_dir, 'LAI_Residual_Analysis.png'));
fprintf(' 残差分析图已保存
');
end
%% ========================================================================
% 完成
%% ========================================================================
fprintf('
========================================
');
fprintf('程序运行完成!
');
fprintf('========================================
');
fprintf('输出文件位于: %s
', output_dir);
fprintf(' 1. LAI_TimeSeries_Results_2020.csv - 反演结果CSV
');
fprintf(' 2. Validation_Statistics.csv - 精度统计
');
fprintf(' 3. LAI_TimeSeries_Comparison.png - 时间序列对比图
');
fprintf(' 4. LAI_Scatter_Plot.png - 散点验证图
');
fprintf(' 5. LAI_Residual_Analysis.png - 残差分析图
');
fprintf('========================================
');
上述代码的实现依赖于一些核心的代码包,可以私信小编联系。
5 反演结果
(1)站点附近小区域的LAI反演
本次选用以站点经纬度为中心点附近5km×5km的区域,通过全局优化算法展开函数求解,进行LAI反演,并将得到的结果和地面测量数据以及MODIS的反射率产品进行对比。得到的结果如下:
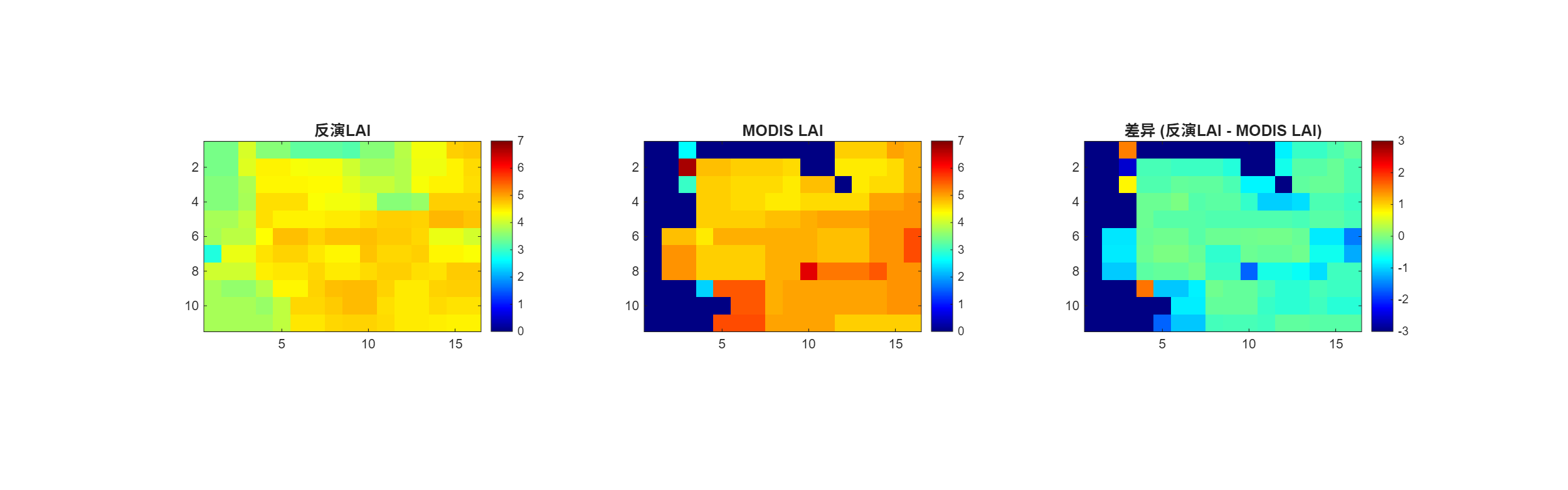
图 考虑先验信息下的反演结果-森林站点
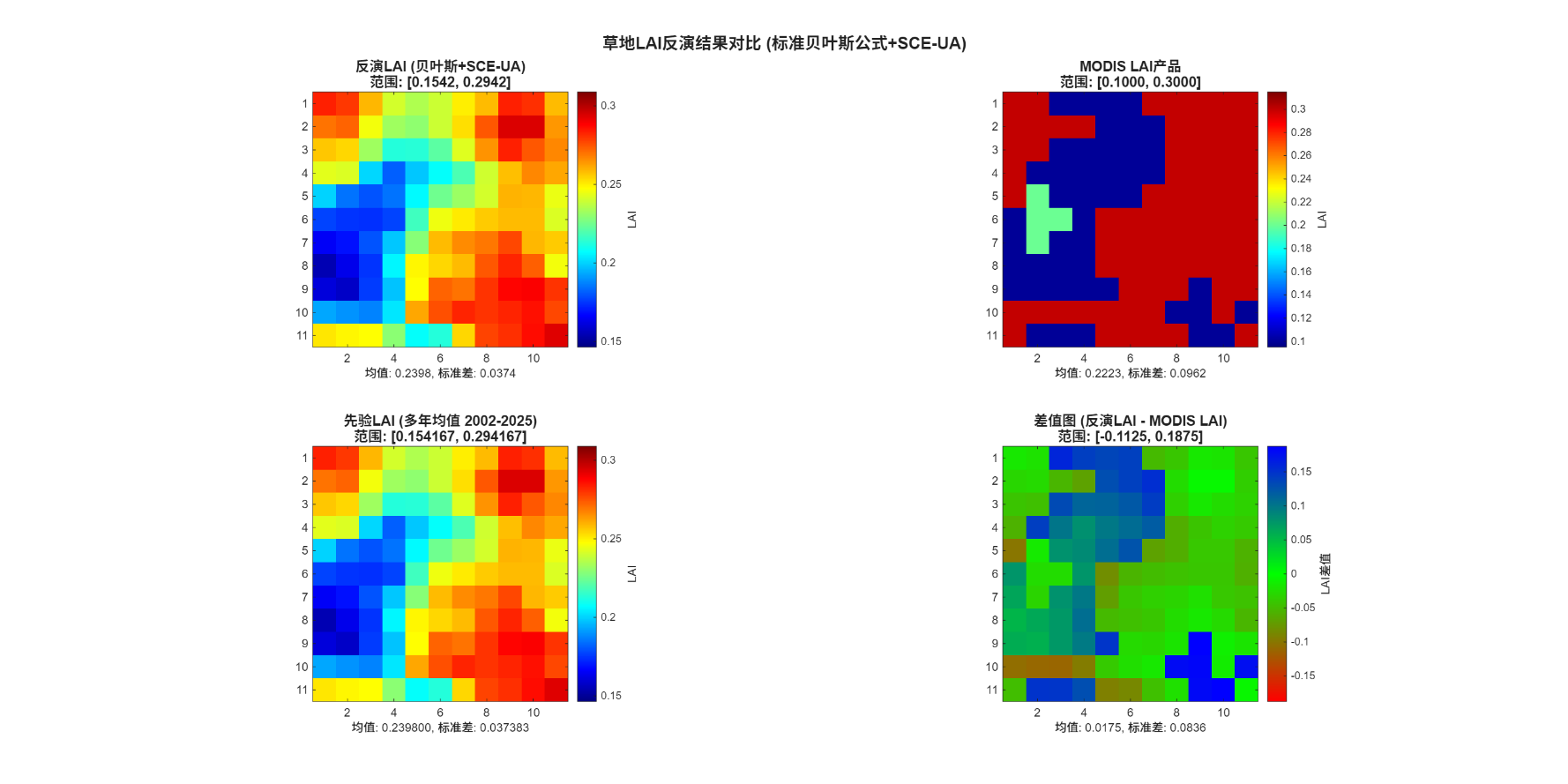
图 考虑先验信息下的反演结果-草地站点
(2)站点所在像元一年的LAI值反演
反演站点所在像元一年的时间序列时,实习过程用的代价函数并没有考虑先验信息。
从趋势上看,反演的LAI时间序列在趋势上基本吻合了MODIS产品的LAI时间序列。据图,发现夏季的反演效果相对较好,两条线比较接近,反演的LAI略低于MODIS的叶面积指数。同时两数据的差值最小,尤其是在7月-9月;冬季反演的的效果比较差,反演的LAI显著高于MODIS的产品。
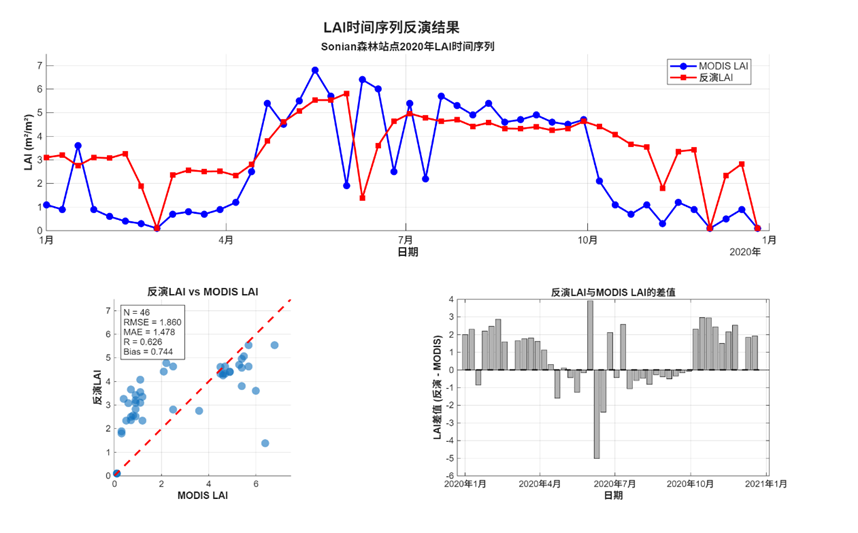
从指标评估来看,反演的LAI和MODIS提供的LAI拟合系数能够达到0.626,均方根误差为1.86,MAE为1.478,总体而言反演的精度相较于站点的小区域LAI精度要高。当然,如果能够纳入多年同一像元的LAI数据作为先验信息输入,或许能够进一步提供LAI模拟的精度。
6 学习总结
遥感反演是一项复杂的任务,病态反演问题告诉我们,实现完美的反演过程只是一种理想,我们工作的重心更应在于如何管理与约束算法求解过程的不确定性,尽管结果有待提高,但仍然是一次不错的尝试!
以上是本期关于遥感反演LAI指数的全部内容啦,欢迎交流!